Introduction
A deep learning model generally works well when it has a huge amount of data. In general, the more data we have better will be the performance of the model.
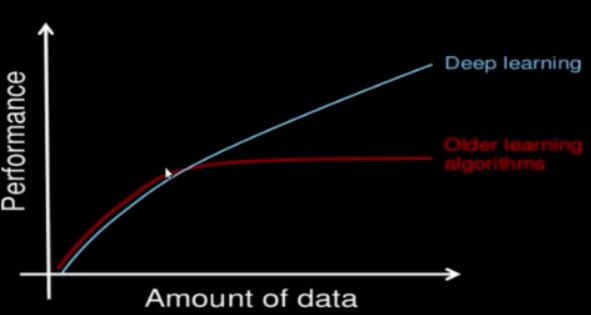
From the graph above, we can notice that as the amount of data increases the performance of the deep learning model also improves. But acquiring a massive amount of data is itself a major challenge. Every time it is not possible to have a large amount of data to feed the deep learning network.
The problem with the lack of a good amount of data is that the deep learning model might not learn the patterns or the functions from the data and hence it might not perform well.
So in order to deal with this and spending days manually collecting the data, we make use of Image Augmentation techniques.
Image Data Augmentation
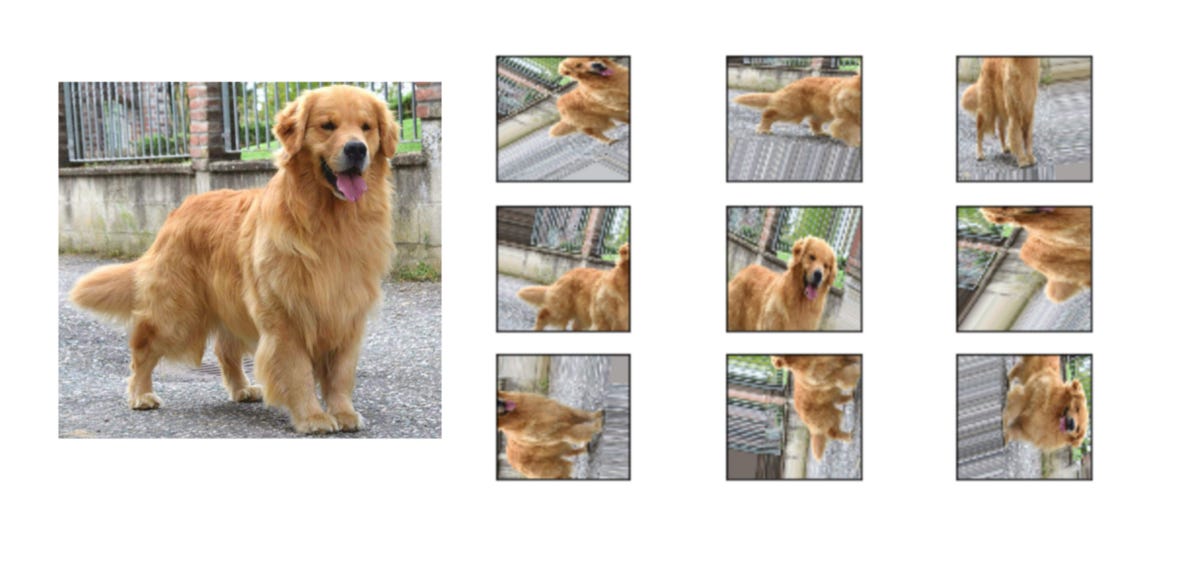
Image data augmentation is a method that can be used to increase the size of a training database by creating modified versions of images in the database.
It is a process of taking the images that are already present in the training dataset and manipulating them to create many altered versions. This not only provides more images to train on, but also help our classifier to expose a wider variety of lighting and coloring situations thus making it a more skillful model.
In the above figure, since all these images are generated from training data itself we don’t have to collect them manually. This increases the training sample without going out and collecting this data. Note that, the label for all the images will be the same and that is of the original image which is used to generate them.
Point to be noted is that Image data augmentation is typically only applied to the training dataset, and not to the validation or test dataset. This is different from data preparation such as image resizing and pixel scaling; they must be performed consistently across all datasets that interact with the model.
Image Augmentation With ImageDataGenerator
The Keras deep learning library provides the ability to use data augmentation automatically when training a model.
A range of techniques are supported, as well as pixel scaling methods. Few of them are:
Image shifts via the width_shift_range and height_shift_range arguments.
Image flips via the horizontal_flip and vertical_flip arguments.
Image rotations via the rotation_range argument
Image brightness via the brightness_range argument.
Image zoom via the zoom_range argument.
Here in this article we will be restricting ourselves to the image augmentation by shifting the width range only, further augmentation like flipping the images, brightness and contrast, rotation etc. can be done by slight modification in the Hyper Parameters.
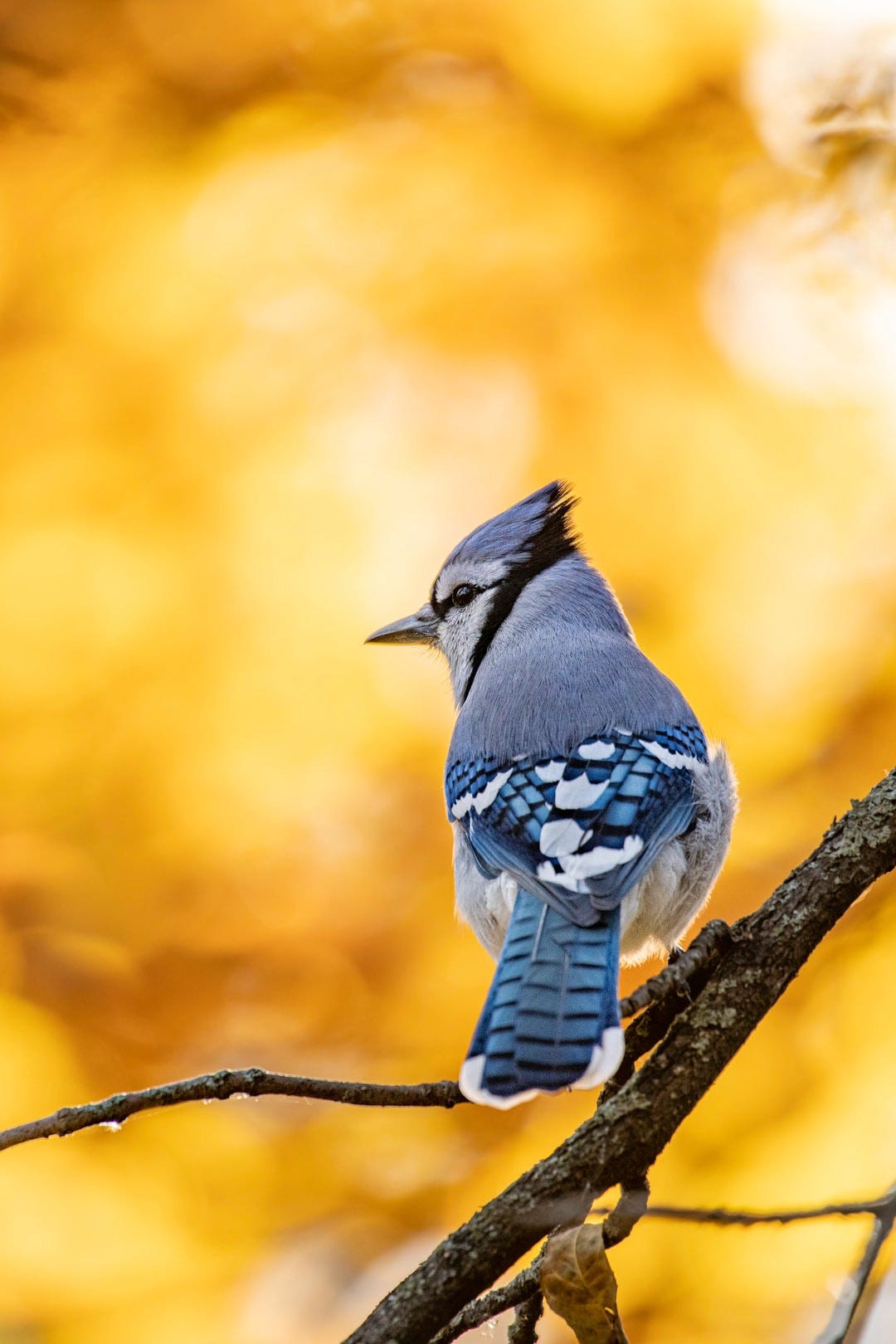
Let us take the following image for augmentation purpose.
Importing Libraries
from numpy import expand_dims
from keras.preprocessing.image import load_img
from keras.preprocessing.image import img_to_array
from keras.preprocessing.image import ImageDataGenerator
from matplotlib import pyplotLoading the image and preprocessing it.
# load the image
img = load_img('bird.jpg')# convert to numpy array
data = img_to_array(img)# it is a function of numpy which expand dimension to one sample in specified axis here 0 that is horizontal
samples = expand_dims(data, 0)Creating image data augmentation generator and preparing iterator.
# create image data augmentation generator
datagen = ImageDataGenerator(width_shift_range=[-200,200])#the width_shift_range and height_shift_range arguments to the ImageDataGenerator constructor control the amount of horizontal and vertical shift respectively.# prepare iterator
it = datagen.flow(samples, batch_size=1)Plotting the augmented images
# generate samples and plot
for i in range(9):
# define subplot
pyplot.subplot(330 + 1 + i)
# generate batch of images
batch = it.next()
# convert to unsigned integers for viewing
image = batch[0].astype('uint8')
# plot raw pixel data
pyplot.imshow(image)# show the figure
pyplot.show()End Notes
To summarize, If we are aiming to develop a robust and generalized deep learning model but do not have a large dataset, In such cases, image augmentation techniques come as a savior, as they allow us to generate a wide range of new data without much effort.
Credits
The above article is sponsored by Vevesta.
Vevesta: Your Machine Learning Team’s Collective Wiki: Identify and use relevant machine learning projects, features and techniques.
100 early birds who login to Vevesta will get free subscription for 3 months.
Subscribe to our weekly newsletter to stay updated on latest machine learning/MLOps articles.
References






